In an age where technology continually reshapes our understanding of security and surveillance, the role of GPS-based spy equipment has become increasingly significant. This specialized technology offers a range of tools designed for tracking, monitoring, and gathering intelligence, serving various purposes from personal security to corporate espionage. As we explore the realm of GPS spy equipment, we will delve into the different types of devices available, their applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding their use. Whether for safeguarding loved ones or managing business assets, understanding the capabilities and limitations of GPS spy equipment is essential in navigating the complex landscape of modern surveillance.
Understanding Spy Equipment and GPS Technology
Spy equipment has evolved significantly over the years, primarily driven by advancements in technology. Today’s spy gadgets are smaller, more sophisticated, and easier to use, making surveillance and tracking more accessible to both professionals and amateurs alike. The integration of GPS technology into these devices has revolutionized the field, enabling real-time location tracking and data collection that was previously unimaginable. Key features of modern spy equipment include:
- Compact Design: Many devices are now designed to fit easily into everyday items, such as watches, pens, or even keychains.
- Real-Time Tracking: GPS-enabled devices can provide instant updates on locations, ensuring continuous monitoring.
- Data Encryption: Advanced tech safeguards against unauthorized access to sensitive information.
When selecting spy equipment, understanding how GPS technology complements these tools is crucial. It allows for the tracking of movement patterns and historical data, which can be invaluable in various scenarios—from personal safety to corporate espionage. Additionally, the interoperability of devices enhances their functionality; for instance, many cameras and drones now come equipped with built-in GPS, offering insights into both visual and locational data. Below is a simple comparison table highlighting different types of spy equipment that utilize GPS technology:
| Device Type | Key Feature | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Tracker | Real-time location sharing | Personal or vehicle safety |
| Hidden Cameras | Remote access & monitoring | Surveillance operations |
| Drones | Aerial monitoring with GPS waypoints | Property surveillance |
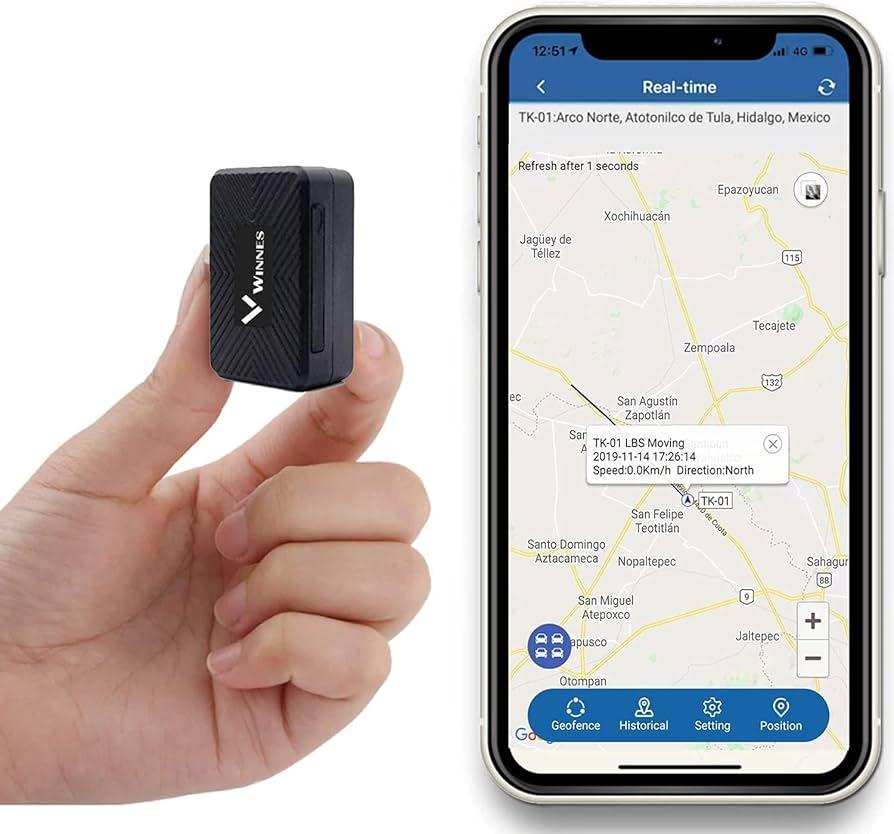
Key Features of GPS Tracking Devices for Surveillance
GPS tracking devices designed for surveillance offer a myriad of features that enhance visibility and control over subjects or assets. These devices are often compact and discreet, making them easy to conceal. A few noteworthy attributes include:
- Real-Time Tracking: Users can monitor the device’s location in real-time through a user-friendly interface, allowing for immediate updates on movements.
- Geofencing: This feature enables users to set virtual boundaries and receive alerts when a device enters or exits these predefined zones.
- Long Battery Life: Many models boast extended battery life, ensuring prolonged surveillance without frequent recharging.
- Historical Data: Access to historical tracking data allows users to review past movements, which can be crucial for investigations.
Additionally, many GPS tracking devices are equipped with advanced functionalities that cater to the needs of users in various scenarios. For instance:
- Mobile App Integration: Users can access tracking information and control settings directly from their smartphones, enhancing convenience.
- Multiple User Access: Some devices allow multiple authorized users to monitor the same tracking device, fostering collaboration in surveillance efforts.
- Durable and Weather-Resistant: Built to withstand varied environmental conditions, ensuring reliability in outdoor surveillance.

Applications of GPS Spy Equipment in Various Industries
GPS spy equipment has revolutionized various sectors by providing real-time location tracking and data collection. In the transportation industry, for instance, fleet managers utilize GPS devices to monitor vehicle routes and performance, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs. Businesses can also implement these technologies to ensure the safety of goods in transit, minimize theft, and optimize delivery schedules. Additionally, ride-sharing companies leverage GPS tracking to ensure passenger safety and improve service quality through better route management.
In the security sector, companies adopt GPS spy equipment for valuable asset protection and personnel tracking. This technology assists in monitoring high-risk employees, ensuring they remain within safe locations during assignments. Moreover, retail businesses deploy GPS tracking to analyze customer movements within stores, helping them to optimize product placement and enhance the shopping experience. The health care industry is also seeing benefits, as patient tracking systems allow hospitals to monitor the whereabouts of vulnerable patients, ensuring their safety and timely intervention when necessary.

Legal Considerations When Using GPS Tracking Devices
When considering the implementation of GPS tracking devices, it’s essential to navigate the complex legal landscape surrounding their use. Many jurisdictions have specific laws that regulate how and when these devices can be employed, which can include privacy laws, consent requirements, and data protection regulations. It’s crucial to understand that tracking someone’s movements without their consent may be deemed illegal in many regions, which can result in serious legal ramifications. Individuals or businesses must be aware of the applicable state or federal laws and ensure compliance to avoid potential lawsuits or criminal charges.
Additionally, organizations using GPS tracking for employee monitoring should craft clear policies and communicate these to their staff to maintain transparency. This is not only a legal precaution but also fosters trust within the workforce. Some key considerations include:
- Notification: Informing employees that they are being tracked
- Purpose: Clearly stating the reason for tracking, such as for safety or productivity
- Data Handling: Outlining how tracking data will be collected, stored, and shared
Failure to adhere to these legal considerations can result in significant penalties. To provide a comparative view, below is a simple table illustrating common compliance requirements across different regions:
| Region | Consent Required? | Purpose Limitation? |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Varies by state | Yes |
| EU | Yes | Yes |
| Canada | Yes | Yes |

Recommended GPS Spy Products for Different Needs
Choosing the right GPS spy product depends heavily on your specific needs. Whether you’re a concerned parent wanting to monitor your child’s whereabouts, a business looking to keep track of assets, or someone needing to ensure the safety of a loved one, there are tailored devices available. Here are some options that cater to various requirements:
- Personal GPS Trackers: Ideal for tracking children or pets, these compact devices are designed for everyday use, featuring real-time tracking capabilities and geo-fencing alerts.
- Vehicle GPS Trackers: Perfect for fleet management or monitoring a partner’s vehicle, these devices often come with extensive battery life and detailed reporting on vehicle locations and speed.
- Hidden GPS Devices: Disguised as everyday objects, these are suited for discreet surveillance purposes, offering stealthy tracking of individuals without raising suspicion.
- Smartphone GPS Apps: Many apps allow you to monitor your loved ones in real-time using their phones, providing a flexible solution without the need for additional hardware.
| Product Type | Best For | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Personal GPS Trackers | Children & Pets | Real-time updates, geo-fencing, alerts |
| Vehicle Trackers | Fleet Management | Detailed reports, speed monitoring, long battery life |
| Hidden GPS Devices | Covert Tracking | Disguised, stealthy, long-lasting battery |
| Smartphone GPS Apps | Versatile Monitoring | Flexible, accessible, familiar interface |
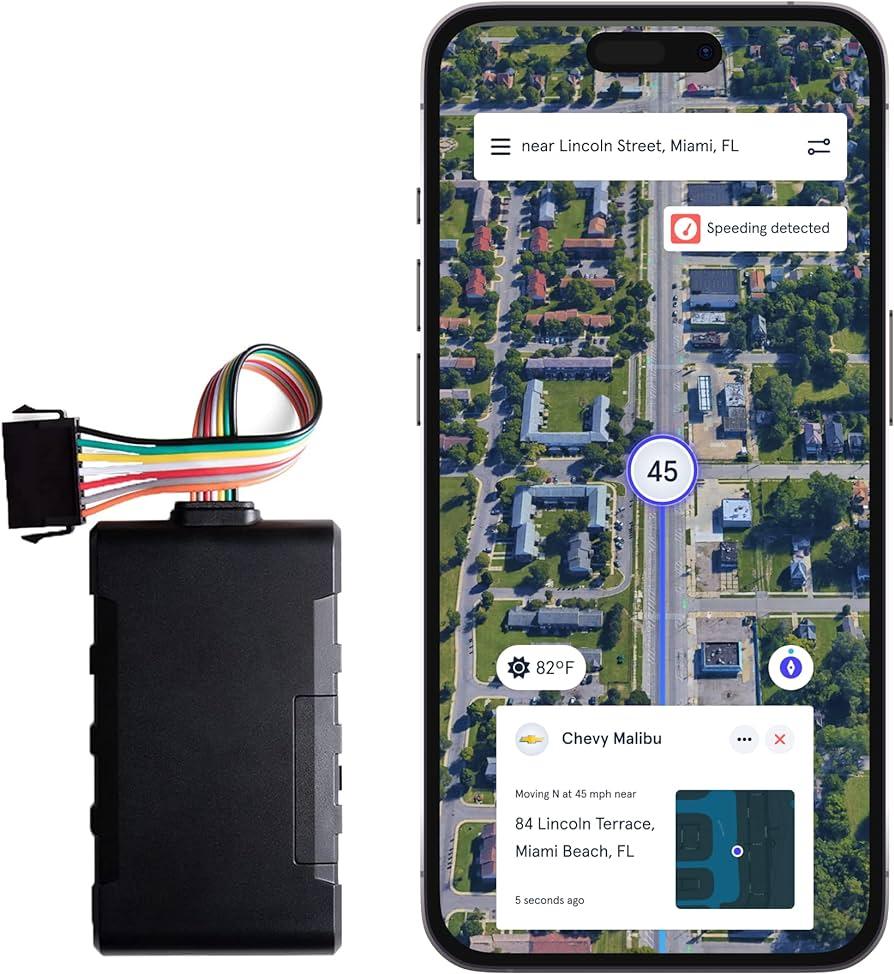
Best Practices for Effective Use of GPS Surveillance Equipment
To maximize the effectiveness of GPS surveillance equipment, it is essential to understand its capabilities and limitations. Start by ensuring that the equipment is properly calibrated to provide accurate location data. Familiarize yourself with the specific features of the device, as many offer customizable settings such as reporting intervals and geofencing options. Regularly update the device’s firmware to maintain optimal performance and take advantage of new features that may enhance its functionality. Proper placement is also crucial; consider environmental factors like coverage areas and potential obstacles that could restrict signal quality.
In addition to technical aspects, ethical considerations must guide the use of GPS surveillance equipment. Respect privacy laws and regulations in your jurisdiction, as unauthorized tracking may lead to legal repercussions. Always obtain the necessary consent when tracking individuals, whether in personal or professional contexts. Implement a robust data management strategy to ensure that collected information is stored securely and accessed only by authorized personnel. Additionally, regularly review the data usage policies to ensure compliance and transparency, fostering trust among all parties involved.
Q&A
Q&A on Spy Equipment GPS
Q1: What is GPS spy equipment?
A1: GPS spy equipment refers to devices that utilize Global Positioning System (GPS) technology for tracking and monitoring the location of people, vehicles, or objects without their knowledge. These devices can vary in size, functionality, and application, from small trackers hidden in personal belongings to more sophisticated systems integrated into vehicles.
Q2: How does GPS tracking work?
A2: GPS tracking works by using a network of satellites that transmit signals to GPS receivers. These signals allow the device to determine its exact location by triangulating its position based on the time it takes for the signals to reach the receiver. The tracked information can then be sent to a monitoring system, often accessible via a computer or mobile app.
Q3: What are common uses for GPS spy equipment?
A3: Common uses for GPS spy equipment include tracking vehicles for fleet management, monitoring children or elderly family members for safety, locating stolen vehicles, and conducting surveillance in security or investigative contexts. Some individuals also use GPS tracking in personal situations to monitor a partner’s movements, although such practices can raise ethical and legal concerns.
Q4: Are there legal considerations when using GPS spy equipment?
A4: Yes, there are significant legal considerations when using GPS spy equipment. The legality of tracking someone without their consent varies by jurisdiction and can depend on the specific context. In many places, tracking an individual without their knowledge can be a violation of privacy rights and may lead to legal repercussions. It is essential to be familiar with local laws regarding surveillance and tracking before using GPS devices.
Q5: Can GPS trackers be detected?
A5: Depending on the type and sophistication of the GPS tracker, they can be detected. Some devices are designed to be discreet and may be hidden within ordinary objects, making them difficult to find. However, more advanced models may emit signals that can be intercepted, and many trackers can be detected using specialized equipment. Targeted individuals may also notice unusual behaviors in their vehicles or items, leading them to suspect tracking.
Q6: What should users consider before purchasing GPS spy equipment?
A6: Before purchasing GPS spy equipment, users should consider the intended purpose of the device, the legal implications of its use, the device’s battery life, accuracy of tracking, ease of use, data storage options, and the level of customer support available from the manufacturer. Additionally, users should weigh ethical considerations, especially when tracking individuals without their knowledge.
Q7: Are there different types of GPS trackers available?
A7: Yes, there are various types of GPS trackers designed for different use cases. Some common types include real-time trackers that constantly update location data, passive trackers that store location data for later retrieval, and OBD-II trackers that plug directly into a vehicle’s onboard diagnostics port. Other options include discreet trackers designed for hiding and wearable devices for personal tracking.
Q8: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using GPS spy equipment?
A8: The advantages of using GPS spy equipment include the ability to monitor and track movements in real-time, enhance security for valuable assets, and provide peace of mind in personal safety situations. However, disadvantages include potential legal issues, invasion of privacy concerns, and ethical dilemmas, particularly in personal relationships. Furthermore, over-reliance on such technology can lead to mistrust between individuals.
Q9: How can consumers ensure their GPS tracking is secure?
A9: Consumers can ensure their GPS tracking is secure by choosing devices from reputable manufacturers that prioritize data encryption and user privacy. Regularly updating software and firmware, using strong passwords for monitoring accounts, and being cautious about sharing tracking information can also help enhance security and protect against unauthorized access.
Q10: Where can GPS spy equipment be purchased?
A10: GPS spy equipment can be purchased from various sources, including specialized electronics retailers, online marketplaces, and dedicated surveillance equipment stores. When purchasing such devices, it is important to verify the credibility of the seller and ensure that the products meet legal standards and regulations in your area.
Final Thoughts
the use of GPS technology in spy equipment has significantly transformed the landscape of surveillance and tracking. With advancements in miniaturization and connectivity, modern devices offer enhanced capabilities that enable users to gather intelligence discreetly and efficiently. Whether utilized in personal security, law enforcement, or intelligence operations, the applications of GPS in spy equipment continue to evolve, raising important considerations regarding ethics and privacy. As this technology develops, it is vital for users to remain informed about the legal implications and best practices associated with its use. Understanding the advantages and challenges of GPS-enabled spy equipment will empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions in an increasingly interconnected world.





